Would you propose to your partner with a ring pop on your second date? Would you yell profanity at your grandma’s church choir performance to make a good impression?
When it comes to the way you communicate with your customers as they form a relationship with your company, it’s all about serving them the right message in the right context at the right time. Matching the tone, type, and frequency of a message with the stage and context your users find themselves in leads them closer to the conversion you’re hoping for. That’s where user journey mapping comes in.
Omnichannel customer journey mapping is a critical way for you to understand and meet your customers’ needs across every communications touchpoint with your brand in order to draw them towards the desired objective. Customer journey maps visualize how a customer interacts with your brand by defining events, motivations, and friction points in their product experience.
Defining customer journeys allows you to refine your messaging strategy in order to meet your customers with the right message at the right time on the right channel.
What is a Customer Journey Map?
The customer, buyer, or user journey, is a visual representation of your customer’s end-to-end experience with your brand. A customer journey charts your customers’ key interactions with your company across multiple channels and throughout their lifecycle.
Understanding Omnichannel Customer Journey
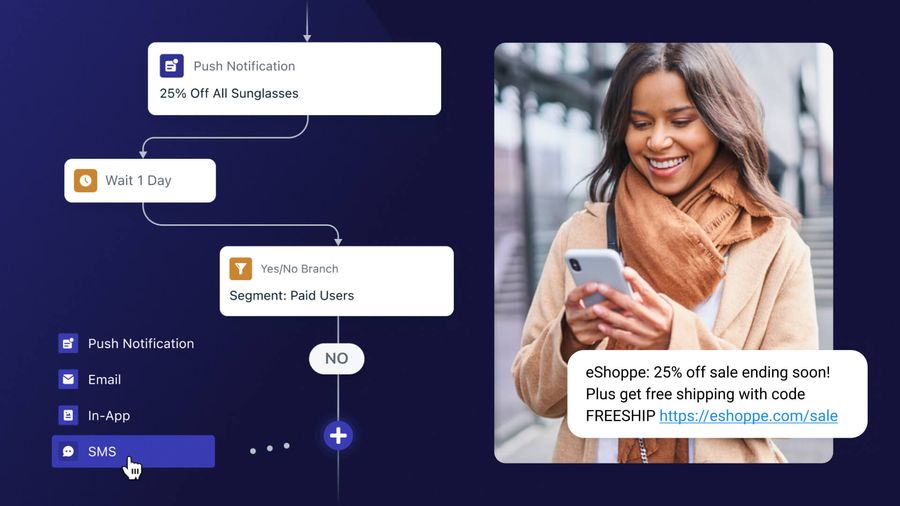
An omnichannel customer journey map includes the series of interactions a customer takes with your brand among the various channels you’ve deployed, including push notifications, SMS, email, in-app messages, and web notifications. Unlike multichannel messaging, which can be fragmented both for the customer and the marketer, an omnichannel marketing approach integrates communication across all customer touchpoints and views each channel interaction as part of one larger conversation. This approach seeks to create a more dynamic, personal, and unified customer journey.
These distinct interactions can include channel behavior, buying behavior, and other triggers such as location, in-app behaviors, conversion types, and more.
Why You Need a Customer Journey Map
Customer journey mapping is valuable in that it gives you a holistic view of customer interactions with your brand, which in turn can inform your messaging strategy to strengthen and scale your cross-channel campaigns.
Here are five reasons you need customer journey mapping as part of your omnichannel messaging strategy.
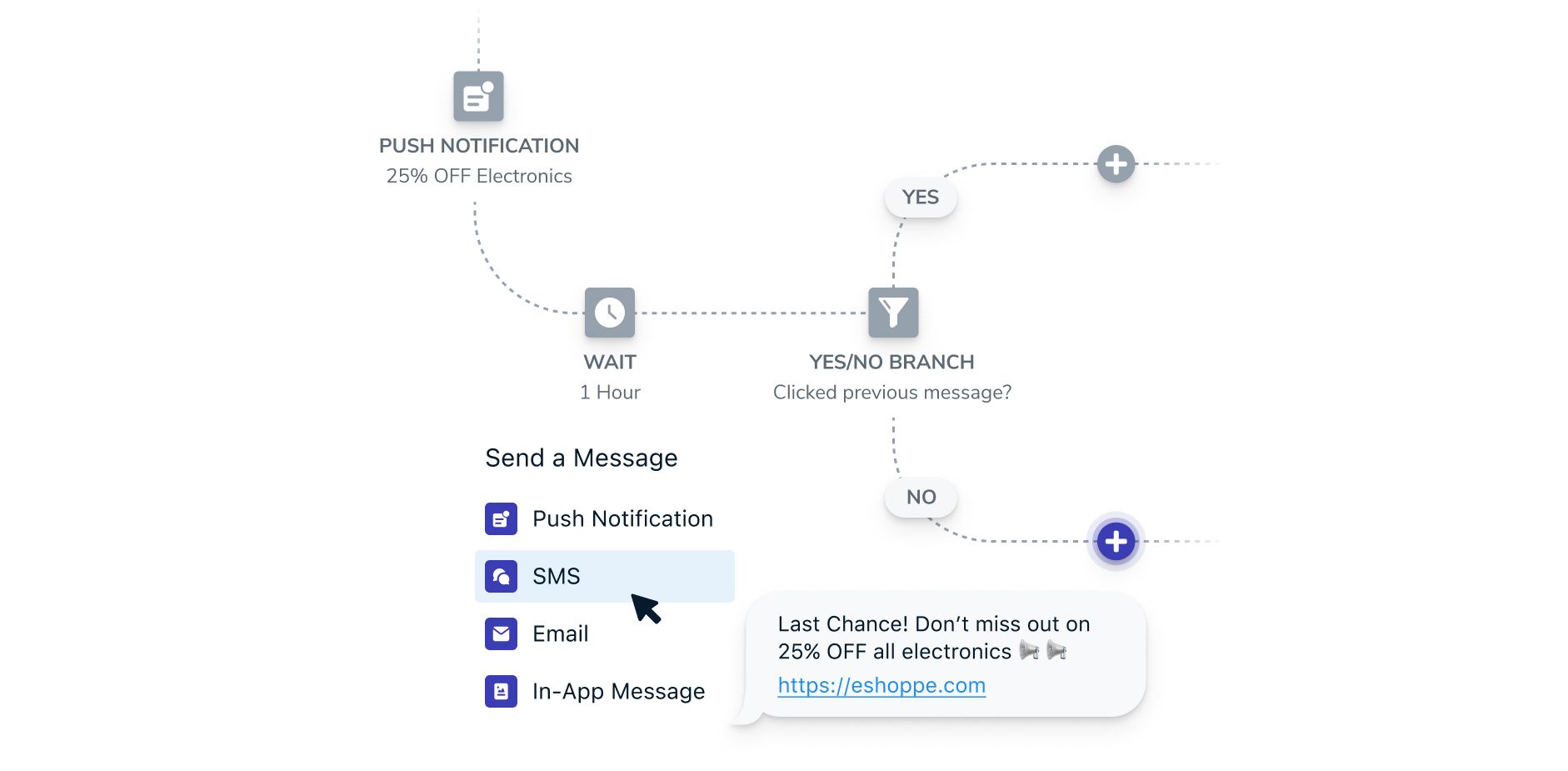
1. Personalize Your Customer Experience (CX)
Consumer expectations for personalized brand experiences are skyrocketing. Customer journey maps allow you to deliver on this desire for increased personalization by communicating tailored and contextually relevant messages in a way that resonates. Although it’s impractical to customize interactions for every single consumer you serve, journeys allow you to optimize end-to-end mobile experiences by prioritizing key audiences and their needs as they complete tasks.
2. Increase Customer Satisfaction
The seamless and personalized omnichannel experiences you deliver based on user mapping lead to higher levels of customer satisfaction, as your customers are being heard and responded to in a way that feels right for them. As customer satisfaction increases, so too does your company’s revenue, studies show.
3. Leverage Your Customer Data
Effective journey mapping aggregates customer data across your tech stack, which gives you a powerful basis for personalizing messages. In this way, you can create complex audiences enriched by multiple information sources and use them as a basis for optimizing your journeys.
4. Put Customer Needs First
Customer journey maps place the customer at the center of your campaign strategy. Customer centricity is key to understanding what messages consumers need to hear at what stage of their journey to push them towards the next milestone, and in turn what will drive the best results for your campaigns. With journey mapping, you’ll better understand different personas’ movement through the funnel, including where they fall off, where they stick, and what types of messages can cater to their needs at each of these points.
For example, if your customer journey mapping exercise reveals that users tend to churn three days after downloading your app, you might set up a re-engagement sequence targeting this audience at this specific touchpoint. Maybe you send them a friendly onboarding email on day three followed by a push reminder on day four.
5. Steer Product Development
Customer journey mapping can give you insights into the areas you should prioritize in your product roadmap. Understanding your customers’ needs along a series of touchpoints can reveal gaps in the product experience, which in turn can drive product development efforts by tracking what consumers actually care about and what moments define their experience with your brand. The data you glean with journeys can help you identify moments where users are most likely to stick or churn. As a result, you can adapt your product based on the journeys you map and iterate on them over time.
Steps to Create a Customer Journey Map
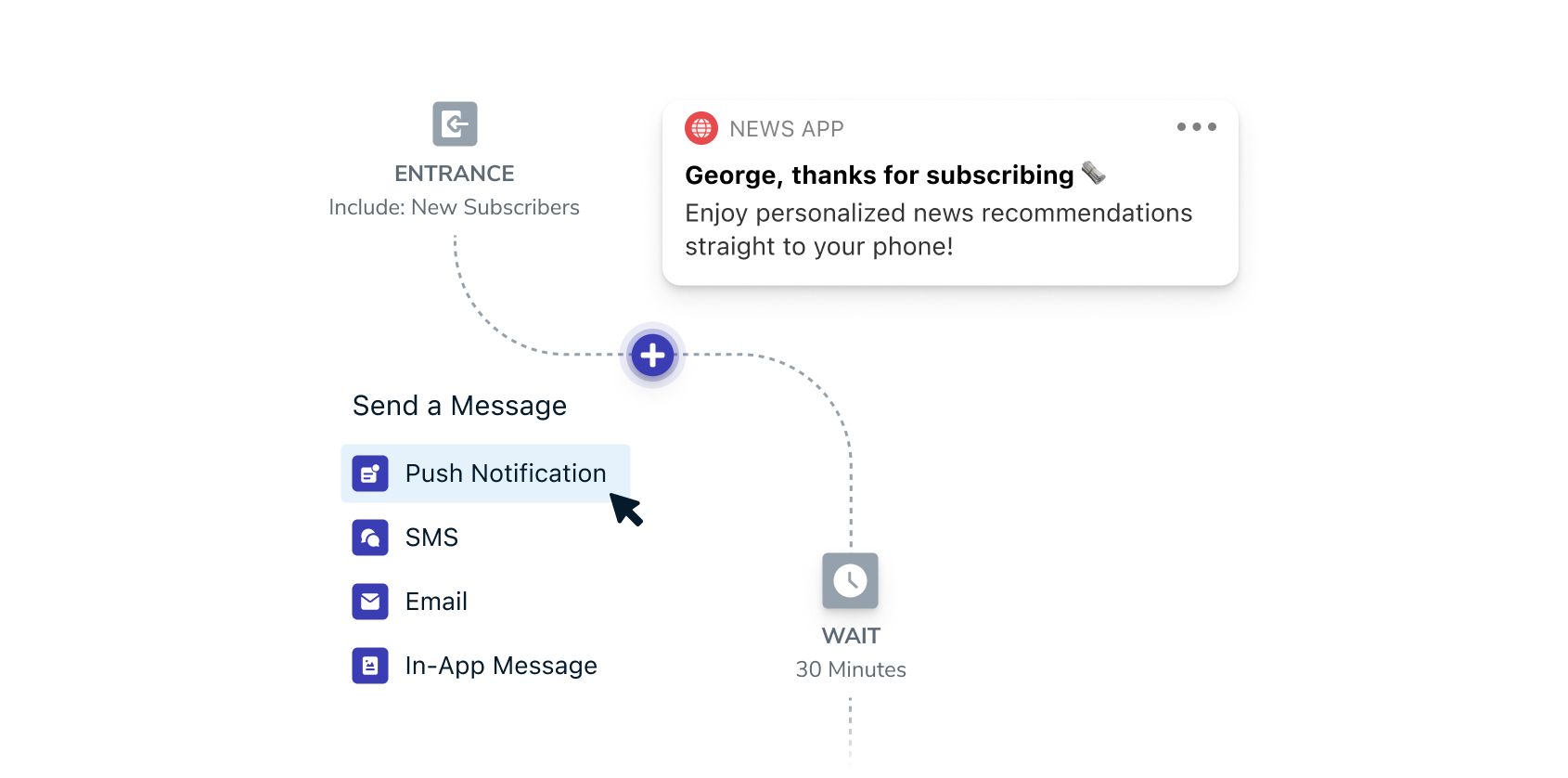
1. Define Your Goal
What’s the goal you’re optimizing your journey for? What’s the desired action you want your customer to take? What’s the ROI you’re looking to improve? You need to define your endpoint before you can define the intermediate steps customers take along their path to purchase.
The desired action you map to could be a purchase, a subscription renewal, or a certain engagement milestone like reaching Level 8 in your mobile game. You can choose to map the high-level customer journey or zero in on a piece of it, like successful onboarding, for example. Your strategy should eventually expand to include multiple journeys that you define based on the existing data you have on your customers.
2. Compile Your Data
Before mapping your customer journey, you’ll want to centralize and refer to the customer data you’ve collected internally and across your tech stack . You can draw from both quantitative data sources —such as your analytics, CDP, and CMS, providers— and qualitative data sources —such as interviews, surveys, and task analyses— in this process.
Your data lay the foundation for an effective journey map. You should take the time to collect and analyze this information so you can build robust customer profiles catered to the audiences that matter most.
3. Define Key User Groups
When understanding a customer’s path across your brand’s messaging touchpoints, you should first identify how different audiences distinctly interact with your product or service and build personas accordingly. It’s valuable to map out multiple journeys to see the best results in your messaging campaigns, because different user groups will take different twists and turns on their path to purchase.
For example, maybe you notice that your Millennial customers tend to discover your brand via social media platforms and convert via deals sent over SMS, whereas Baby Boomers are more likely to discover you via organic search and make purchases after clicking on your brand’s emails. You could create two buyer personas based on these insights and map out two distinct journeys outlining each persona’s touchpoints with your brand. Consider their distinct motivations, behaviors, pain points, and channel preferences as you map the steps they take towards the conversion you’ve defined.
4. Map Out Your Touchpoints
Finally, it’s time to bring the pieces together and sketch out your user journey based on all the data you’ve gathered. Bring together all your research and flesh out your timeline with the key touchpoints you’ve identified for each user persona. Remember that touchpoints are the building blocks of your journey. They are points of contact consumers have with your brand on any channel as they progress towards the objective in question.
Consider positive, negative, and neutral interactions a customer has with your brand on each channel you provide, and how they seamlessly, or not so seamlessly connect the customer experience.
Here’s an example of an omnichannel customer journey a user of your food delivery app takes to place an order.
- Touchpoint 1: Customer installs food delivery app
- Touchpoint 2: Customer browses local burger joint options in the app
- Touchpoint 3: Customer receives retargeting email offering a free delivery promotion at the local burger joint
- Touchpoint 4: Customer places order in the app
- Touchpoint 5: Customer receives order updates via push
- Touchpoint 6: Customer receives order
5. Optimize as You Go
As your product experience and the digital marketing ecosystem evolve, so will your customer journeys. Be prepared to modify, expand on, and even (metaphorically) burn old customer journey maps as you go. It’s all part of the process of understanding your unpredictable human customers and their ever-changing needs. Prepare to validate your assumptions along the way with testing, remembering to optimize for the ROI of your campaigns.
Get Started with OneSignal
OneSignal is designed to help you send notifications and seamlessly manage your user communication across every channel, including mobile push notifications, web push notifications, bulk SMS, in-app messaging, and email.
With our Journeys Builder tool, it's easy to create cross-channel messaging workflows that are triggered based on real-time user engagement. Our platform is quick to set up and makes it easy to automate and customize messages without doing any development work. If you don't have a OneSignal account, you can create one for free and create your first Journey today!
Get Started for Free